left lateral compression test|apley compression and distraction test : exporter exporters exporting With patient standing, sitting, or lying supine, use both hands to compress the lateral sides of the rib cage inward towards the sternum. With the patient lying on their side, use both hands on the lateral side of the rib cage that is facing upward to compress the ribcage towards the table. webEspaços para casamentos - Villa Vezzane. Preços, fotos, opiniões, disponibilidade, telefone e endereço. O espaço ideal para realizar seu .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da In questo caso il metodo che ti andiamo a presentare su come vincere alla roulette online o terrestre, si basa su una famosissima serie numerica conosciuta da centinaia di anni e con un alone di mistero che la segue.Parliamo della serie di Fibonacci composta dai numeri 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, .
With patient standing, sitting, or lying supine, use both hands to compress the lateral sides of the rib cage inward towards the sternum. With the patient lying on their side, use both hands on the lateral side of the rib cage that is facing upward to compress the ribcage towards the table.
Allen Test, Hyperabduction Syndrome Test: Examination type: Neurological : Patient .Empty Can Test: Examination type: Muscle test (strength): Patient & Body Segment .Past Pointing Test: Examination type: Cognitive function, coordination .
Underlying shoulder or elbow pathology may make this test difficult to perform. .Finger-Thumb Test: Examination type: Cognitive function, coordination .Gerber Lift-Off Test - Lateral Compression Test - University of West AlabamaHalstead's Test - Lateral Compression Test - University of West Alabama
Biceps Load Test I - Lateral Compression Test - University of West AlabamaAnterior Instability Test - Lateral Compression Test - University of West .Posterior Drawer - Lateral Compression Test - University of West Alabama
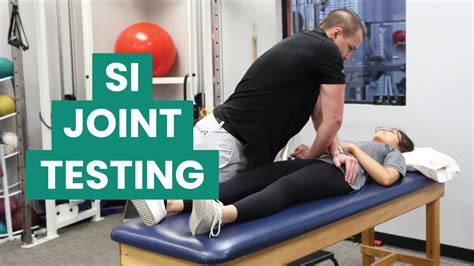
Pelvic ring fractures are high energy fractures of the pelvic ring which typically occur due to blunt trauma. Diagnosis is made radiographically with pelvic radiographs and further characterized with CT scan.Compression Test at the Knee (and Lateral Hip) The compression test can also be done by tapping at the knee, again transmitting pressure towards the hip. Finally, you can also by tap lateral to the hip ( see video for demonstration ). Lateral compression fractures of the pelvis (Young Burgess LC, OTA B1, B2) are the most frequent pelvic injury types and biomechanically the most stable of the unstable . Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is a degenerative condition of the sacroiliac joint resulting in lower back pain. Diagnosis is made clinically with pain just inferior to the posterior superior iliac spine that is made worse with hip .
Types of unstable pelvic fractures: (Left) Anterior-posterior compression fracture. (Right) Lateral compression fracture. In this fracture, the pelvis is pushed inward.
Special mammography views, which may include magnification views or focal/spot compression views. Both are used to make a small area of breast tissue easier to evaluate. Other adjunctive . some of the breast being imaged may get pulled or left out too. To get as much medial tissue as possible, the mammogram technologist will place both . Lateral patellar compression syndrome: . Clinical test for diagnosis of patellofemoral pain syndrome: systematic review with meta-analysis. Phys Ther Sport. 2013;14(1):54-59.The Kemp test (also known as the quadrant test and extension-rotation test) is a provocative test useful for diagnosing pain related to facet joint pathology, e.g. osteoarthritis.. The client performs combined extension and rotation of the .
sij pain provocation tests
Active Compression test ("O'Brien's Test") . Lateral Scapular Winging. test for trapezius weakness or spinal accessory nerve (CNXI) dysfunction. positive if the inferior boarder of the scapula migrates laterally. technique. while standing, have the patient forward flex to 90 degrees and push against a wall (or other stationary object). Pelvic somatic dysfunctions. Types of pelvic dysfunctions. Anterior and posterior innominate; Superior and inferior innominate shear; Innominate outflare and inflare; The ASIS, PSIS, and standing flexion test need to be evaluated to diagnose pelvic dysfunctions.. Examination. Position: supine; Procedure. Perform standing flexion test.; Reset pelvis.. Ask .
The lateral and medial menisci are crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structures that collectively cover approximately 70% of the articular surface of the tibial plateau and primarily function in load transmission and shock absorption through the tibiofemoral joint. They are wedge-shaped with thicker portions at the periphery of the joint, thereby deepening the articular .
Lateral compression fracture; Vertical shear fracture; Types of unstable pelvic fractures: (Left) Anterior-posterior compression fracture. (Right) Lateral compression fracture. In this fracture, the pelvis is pushed inward. Vertical shear fracture. In this . anteroposterior compression: result in an open book or sprung pelvis fractures; lateral compression: result in a windswept pelvis; vertical shear: results in Malgaigne fracture or bucket handle fracture; . X-rays are a quick and simple test that will detect the majority of pelvic fractures. They can be difficult to assess because of the . Lateral recess stenosis is the narrowing of the space within the spinal canal that is located toward the sides. Learn how treatment can ease symptoms. . Myelopathy symptoms result from irritation or compression of the spinal cord. . in which your healthcare provider will test your reflexes and look for signs of pain, weakness, .
Compression Test at the Knee (and Lateral Hip) The compression test can also be done by tapping at the knee, again transmitting pressure towards the hip. Finally, you can also by tap lateral to the hip (see video for demonstration). All compression tests can be positive in hip pain but especially with a fracture.The test also assesses the hip, due to forces being transferred through the joint. The position of flexion, abduction, and external rotation, when combined with overpressure, stresses the femoral-acetabular joint and produces pain, if irritated. . The leg is placed in a figure-4 position (hip flexed and abducted with the lateral ankle resting . INTRODUCTION. Meralgia paresthetica (from "meros," meaning thigh, and "algo," meaning pain) is the clinical syndrome of pain and/or dysesthesia in the anterolateral thigh associated with compression of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is a pure sensory nerve that is susceptible to compression as it courses .
The patient is positioned long sitting in a couch while the medial and lateral aspects of the forefoot of the patient are grasped by the clinician/examiner using one hand. The examiner then proceed to squeeze the medial and lateral parts of the foot earlier grasped with a hand while the tender area is palpated with the other hand.Begin with a standing flexion test (Figure 1) to determine laterality of the dysfunction.The side of the dysfunction is determined by the superior PSIS. Alternatively, perform the ASIS compression test, with the patient supine, by compressing bilaterally anterior to posterior at the ASIS.The Cervical Flexion-Rotation Test (CFRT), in contrast to other forms of manual examination, is an easily applied clinical test purportedly biased to assess dysfunction at the C1-C2 motion segment. . The patient's head is then rotated to the left and the right; If a firm resistance is encountered, pain provoked, and range is limited before .The most common place for compression of the nerve is behind the inside part of the elbow. Ulnar nerve compression at the elbow is called cubital tunnel syndrome. . (Left) Photo shows the . During the test, small needles are put .
The Apley's grind test (Apley Compression test) is used to evaluate individuals for problems of the meniscus in the knee. This test is named after Alan Graham Appley (1914 . The transverse (inter-meniscal) ligament is anterior and connects the medial and lateral meniscus. The coronary ligaments connect the meniscus peripherally.
si compression and distraction test
air permeability testing
Valsalva test. radicular pain not worsened by Valsalva as is the case with a herniated disc. normal neurologic exam. . obliteration of perineural fat and compression of lateral recess or foramen. facet and ligamentum hypertrophy. MRI findings of spinal stenosis may found in asymptomatic patients. CT myelogram. more invasive than MRI.
Core Tip: To summarize, superior mesenteric artery syndrome (SMAS) is a rare condition that occurs when the superior mesenteric artery compresses the third part of the duodenum. This compression can cause obstructive symptoms and weight loss. SMAS can be caused by a variety of factors, including abnormal anatomy, rapid weight loss, and previous abdominal .Postoperative blood test. After pelvic surgery, routine hemoglobin and electrolyte check out should be performed the first day after surgery and corrected if necessary. . Detailed step by step desription of Operative treatment for Incomplete disruption of posterior arch, lateral compression fracture located in our module on Pelvic ring. Weakness: Muscle weakness, particularly in the legs, can occur as nerve compression progresses. Diagnosing Lateral Recess Stenosis. To diagnose lateral recess stenosis, your healthcare provider will perform a thorough evaluation, which may include: . MRI is considered the gold standard test. MRI is a highly effective tool for visualizing soft . Subacromial impingement is the most common cause of shoulder pain which occurs as a result of compression of the rotator cuff muscles by superior structures (AC joint, acromion, CA ligament) leading to inflammation and development of bursitis. . positive Hawkins test . positive if internal rotation and passive forward flexion to 90° causes .
Chronic anterior knee pain with a stable patella is often associated with overload and increased pressure on the lateral facet due to pathologic lateral soft-tissue restraints. “Lateral pressure in flexion” is a term describing the pathologic process of increasing contact pressure over the lateral patellar facet as knee flexion progresses. This report describes a .The test is positive if you experience: Grinding noise. Inability to contract the quad with pressure on your knee. Pain. A positive test may mean that the cartilage under your patella is wearing down. The test is negative if you don’t experience any issues during the test.Foraminal stenosis is a condition that happens when narrowing in parts of your spine causes compression of your spinal nerves. Most cases don’t cause symptoms, even with severe narrowing. However, when there are symptoms, pain and nerve-related issues can happen. There are many possible treatments, ranging from rest and physical therapy to .
Patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS) is a broad term used to describe pain in the front of the knee and around the patella, or kneecap. It is sometimes called "runner's knee" or "jumper's knee" because it is common in people who participate in sports — especially females and young adults — but PFPS can occur in nonathletes, as well.
The 3 injury mechanisms described by the Young-Burgess classification are anterior-to-posterior compression (APC), lateral compression, . The best screening test for a pelvic fracture is an anteroposterior (AP) pelvic radiograph. This study can show most pelvic fractures. Trauma patients typically undergo routine abdomen and pelvis CT scans.
air permeability test textiles

posterior shear test si joint
Resultado da aposta segue padrão o que significa. Opinião. Opinião. aposta segue padrão o que significa. 2024-01-16 01:51:12. Expansão de WoW: Warlord .
left lateral compression test|apley compression and distraction test